Pink Sheep
A story that both terrified and intrigued me.
Simple reason they were lied to
https://gateway.ceh.ac.uk/terraCatalog/Start.do search chernobyl and click the vegetation result
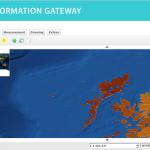
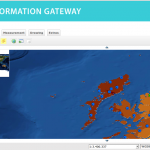
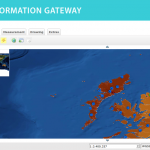
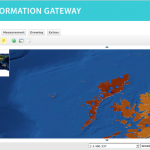
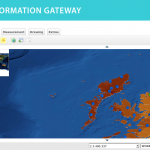
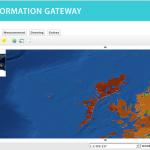
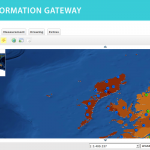
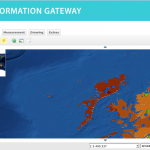
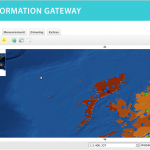
Following the 1986 Chernobyl accident, CEH (formerly ITE) conducted a number of surveys of radionuclide levels in soil and vegetation from throughout Great Britain. The sample locations presented here are linked to data available from the CEH Information …
view (1.3.0)

- Description
- Categorisation
- Access
- Distribution
- Quality
- Metadata
Description
| Title: | Post-Chernobyl soil and vegetation surveys (1986-1987) – map of sample locations | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alternate title: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abstract: | Following the 1986 Chernobyl accident, CEH (formerly ITE) conducted a number of surveys of radionuclide levels in soil and vegetation from throughout Great Britain. The sample locations presented here are linked to data available from the CEH Information Gateway and refer to three sampling dates: May and October 1986 and Spring 1987. The data are suitable for interpolation to create spatially variable surfaces suitable for input into models. Example surfaces have been generated for Cs-137 activity concentration in vegetation in spring 1986 and Cs-137 Bq/m2 in upper soil layers for both autumn 1986 and spring 1987 (the latter covering Scotland only). The data (available for download by searching for ‘Post-Chernobyl soil and vegetation surveys (1986-1987)’) are for vegetation, upper and lower soil in May 1986 (vegetation only), October 1986 and Spring 1987. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Resource Reference Date: |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other Citation Details: | – | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Responsible Party: |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Responsible Party: |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Responsible Party: |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spatial Reference System: | urn:ogc:def:crs:EPSGCRS:84 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Geographic Location (extentTypeCode: ): |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Extent: | – | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Temporal Extent: |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vertical Extent: | – – – |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| URI Codespace: | – | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unique Resource Identifier: | – | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Supplemental information: | – |
So what do you do if you find yourself in this situation?
Personally knowing that suspected radionuclide were no doubt in the blood and Urine- testing for these with and 24 hour urine test and making sure a A technique “whole-body counting” was used .
Damage to blood can be found for a start by
“Among biological methods of dosimetry the cytogenetic method is undeniable the most widely spread and best studied. This method is based on the analysis of the frequency of chromosome aberrations in blood lymphocytes of the human organism exposed to radiation. Standard dose effect curves are obtained after in vitro irradiation of blood cells for quantitative determination of the doses of exposure. By comparing the data on the frequency of cells with chromosome aberrations with a calibration curve it is possible to estimate the irradiation dose. Radiation may cause two types of chromosome aberrations: unstable (dicentrics, centric rings) and stable (translocations). The most often used for the purposes of biological dosimetry is the frequency of dicentrics and centric rings in peripheral blood lymphocytes. As a rule, the frequency of dicentrics permits estimating the dose of irradiation at early periods after exposure.
· Retrospective dose assessment by the frequency of dicentrics is unfortunately not always possible. This is first of all due to the elimination of cells with unstable chromosome aberrations with time. However, the cytogenetic method for retrospective assessment of irradiation doses is analysis of stable translocations by the FISH method. The frequency of translocations remains constant during a long period (years) after irradiation.”